Many things have changed in the past few years – at breakneck speed! Technology is evolving rapidly – and unstoppable – and with it comes the age of digitalization, playing a major part in all areas of the industry. Digitalization is here to stay!
It’s nothing new, that especially in the entertainment industry digitalization shows what it’s got. And it brings with it incredible changes to the AV interface, that make the audio- and video world that much more versatile and sharp. But what is changing in the transfer of video and audio data between players and playback devices and in the requirements for the connector?
From analog scart connections to digital HDMI transmission, we will show you what you need to know.
Read more, to find out which cable connection is best for your Digital Signage display.
Let’s go back to the beginning of the DVI interface, the first to enable optimal quality in digital transfer between graphic card and modern flat screen displays, moving us away from the analog connection.
Because originally a digital to analog converter (which is built into the graphic card these days) converts the digital data from the graphic card to analog data, so it can be transferred to the monitor from an analog connection (VGA). Since classic analog monitors of course need analog signals to display anything.
Digital Transfer with DVI
Initially even the modern TFT Displays (flat screen monitors) receive their data this way just to then convert the analog signals back to digital data via an analog to digital converter.
Sounds complicated? It is! And a lot of quality gets lost this way.
With the rapid changes to flat screen TVs (LCD or flat panels) the demand for a much more direct way of transferring digital data is growing. Without the need for converting analog signals first.
To sum it up: the display needs digital data, the graphic card provides digital data. So why is there no standard for getting the data from one to the other to prevent any loss of quality?
And this is where DVI comes in. The Digital Visual Interface (DVI) replaces the VGA connection (Video Graphics Array) between the modern monitor and the graphics card.
It works like this:
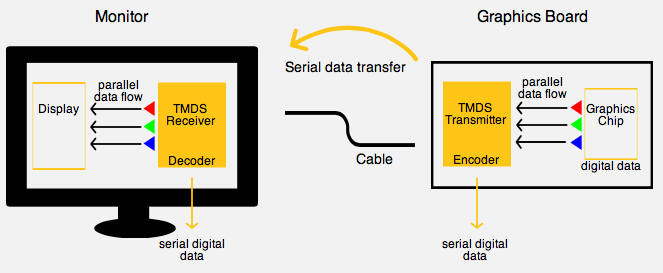
During the digital DVI transmission, digital color data from the graphics chip gets passed on to a TMDS transmitter in a parallel data flow of 24-bit. Here they are encoded into serial digital data. After that, the data is transferred via cable in a serial data transfer to the monitor, which is equipped with a TMDS receiver. This receiver again, decodes the data back to a parallel data flow.
DVI is mainly used in the IT sector as the electronic interface for computers and as a standard for video transmission. Even though there are TVs with a DVI input that can convert signals from digital sources, like a DVD player or a computer, there are different standards in consumer electronics. Mostly because the expectations in this industry are much higher and continue to grow.
Which leads us to our next topic: digital transfer via HDMI
What is HDMI?
HDMI is an advancement on DVI, mostly used in consumer electronics and responsible for digitally transferring video and audio data.
HDMI is backward compatible with DVI, meaning not all HDMI signals can be converted to DVI, not even with adaptors. DVI on the other hand, is upward compatible in most cases. Meaning that such signals as digital signals (DVI-D) or analog and digital signals (DVI-I), can be converted to HDMI with the help of an adapter. So if you happen to already use a DVI cable, you will be able to transmit signals via DVI-D or DVI-I to an HDMI input.
Even though HDMI is used mostly in entertainment electronics, you may also find it in the IT sector. Since there are graphics cards that have a built-in HDMI output, a sort of HDMI adapter.
HDMI DVI Comparison
When comparing DVI and HDMI we can quickly see pro’s and con’s, as well as some qualitative differences regarding their application. The information regarding connection difficulties and wear can seem like a negative point at first, but the quality of the connectors itself, just like the overall quality standards, are consistently adapted and upgraded though.
HDMI however might still be the unique connection among several options. Expanding its lead with the ability to carry uncompressed video as well as uncompressed audio.
When we look at audio quality, HDMI is able to play stereo sound and home cinema atmosphere while DVI will entail the need for an additional cable to transmit audio signals.
Also when using HDMI, anything displayed is subject to copy protection HDCP. Whereas not every DVI connection is suitable for copy protection, so you will definitely have to check the descriptions. Because if the existing connection doesn’t fit CP, the DVD you just bought won’t show an image and the show in HDTV won’t either.
There might be connection problems with HDMI that lead to an outage of audio and visuals. But as mentioned above, this case is pretty rare today since standards are being upgraded consistently.
HDMI Functions
High quality video with no disruption combined with audio transferred at a high frequency rate – this is what HDMI delivers.
High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) gives you a high resolution, in which videos and movies in HD (high definition) and UHD (ultra-high definition) are streamed without image disruptions.
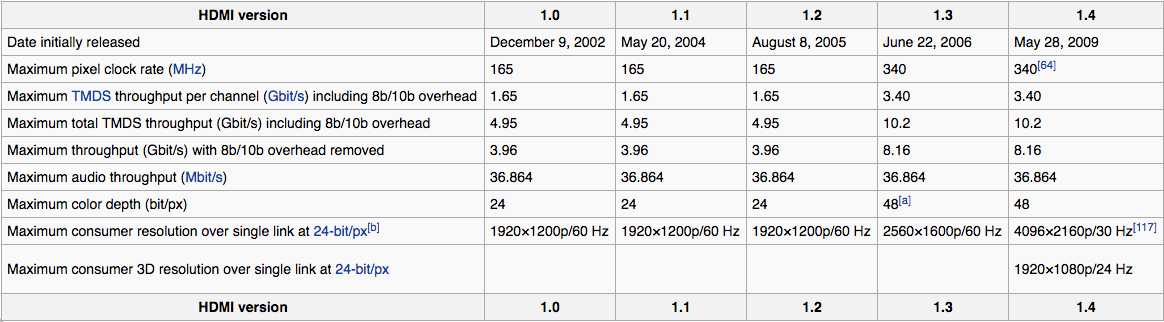
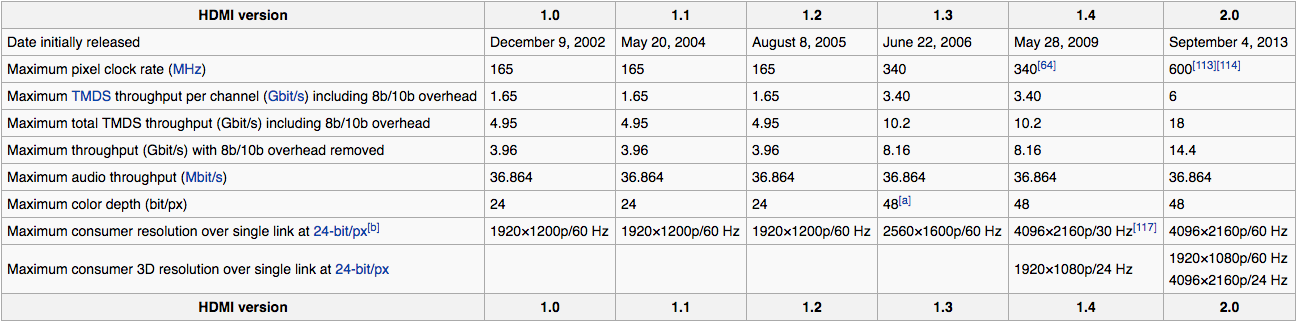
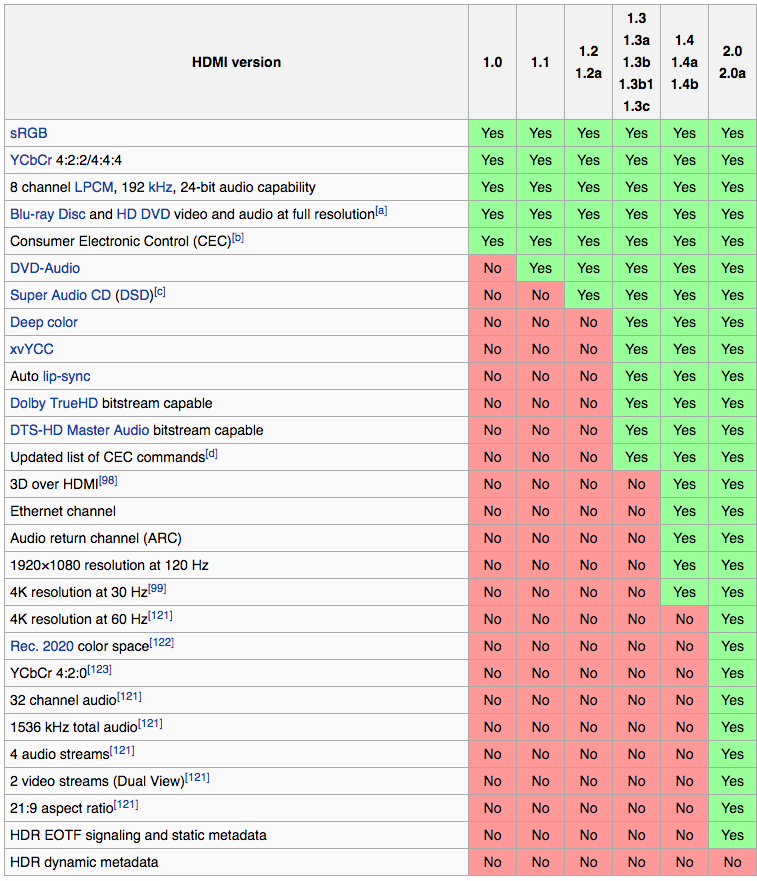
HDMI iterations have been changing at a rapid pace since 2002 to include more and more specifications for the entertainment industry, providing the most in audio and visual quality. Next to continuing improvements in pixel rate, video resolution and audio formats,
we will show you the most interesting additions:
- An integrated HDCP content protection.
Guarding the audio and video material from piracy while it’s being transferred from sender to receiver.
- Since 2005 and the launch of HDMI 1.2 HDMI 1 provides the function of CEC – Consumer Electronics Control.
What does this mean for your home theater? Full control over all your entertainment center electronics that support CEC and that are connected over HDMI. Meaning you can command and control your CEC-compatible TV, Blu-ray player, gaming consoles and sound systems with just one remote.
- Since 2006 and version 1.3, HDMI 1 is able to compensate errors in audio/video timing – Lip Sync.
Which makes audio processing times in devices adjust automatically. For even more TV experience. Syncing audio and visual plays a big role in creating a smooth and brilliant viewing experience. Modern players are capable to lip sync. This feature allows them to delay the playback of the audio to match it just perfectly with the video stream and to therefore avoid that audio and video fall out of synchronization during playback.
- Introducing HDMI 1.4 in 2009, the home entertainment package now includes ARC Function (Audio Return Channel).
This technology is pretty useful and able to significantly simplify home entertainment systems. It simplifies transmission of audio and video through just one HDMI cable. Meaning that while a video is played on your TV (sourced from a Blu-ray-Player for example), the TV can send the audio to an AV receiver, which again transfers the incoming audio signals to a connected external sound bar system, eliminating the need for an audio cable. As long as the devices are equipped with ARC, the components’ power, volume and other features can be controlled from one TV remote.
For a secure and problem free connection, we recommend a cable length no longer than 5 meters (m). Using a cable up to 20 m, will still provide a good connection, but small disruptions may be noticeable. Using cables longer than that can lead to a deterioration in signals and large disruptions. An HDMI-amplifier or extender does help here.
- HDMI 1.4 introduces the feature called Ethernet Channel (Network).
Meaning that all devices that can be connected to the internet can now also be connected with each other easily. The channel technology consolidates video, audio and data streams into just one cable. Which again reduces the amount of cables needed.
- In addition, HDMI 1.4 supports 4K2K, for a clearer, crisper video. This is about 4 times the resolution of a 1080p HD display.
Technical facts of two different resolutions:
- 4096 x 2160 pixel resolution, also 4K, with 24 frames per sec. (24 Hz)
- 3840 x 2160 pixel resolution, Ultra-HD (UHD or Ultra High Definition) or 2160p, with up to 30 frames per sec (30 Hz). This extremely high resolution has 4 times the amount of pixels of the typical video resolution before the newest HDMI, 1080p.
- HDMI 1.4 enables automatic content type recognition.
There is no need for manual settings of a perfect image display. The source device signals the display device which content type will be shown, e.g. if it’s a movie or a sports event. And the display automatically selects the correct viewing mode. This provides the viewer with perfect HD quality every time the content type is changed. Content type recognition also extends into recognizing 3D or 4K content and its unique quality requirements.
- Last but not least: Support of 3D format
But it doesn’t stop here! The evolution of HDMI continues, providing revolutionary, crisper images with HDMI 2.0 and HDMI 2.0a.
However, it’s important to know that all HDMI functions are optional. Which means, that while all HDMI devices will have two audio channels and 480p, all other functions are not necessarily built-in or even supported in all devices.
If this was enough technical background information and you are ready to connect your own Digital Signage display:
More Entertainment with HDMI 2.0 and HDMI 2.0a
HDMI 2.0/2.0a, the newest update and interface as well as AV standard, surpasses its predecessors since 2013 with a significantly increased bandwidth, that allows 4K resolution at 60Hz. Small feature updates have been implemented since 2015.
HDMI 1.4 has a maximal bandwidth of 10,2 Gbit/s, and can only play Ultra-HD or 4K videos with 30 frames per second (2160p30) or 24 frames per second (4K24). Which is completely fine for most movies. HDMI 2.0 with its bandwidth of 18 Gbit/s however can play 4K with 50 or 60 images (4K60 or 2160p60), allowing an Ultra-HD viewing experience without any disruptions.
This is especially interesting for gamers and the entire gaming industry, as well as for fast content videos, like action movies or sports videos.
New features are: en/ctimes.com.tw
en/ctimes.com.tw
- Ultra-HD support and the new HDCP 2.2 content protection
- Even more surround sound with up to 32 audio channels
- HDR support
HDR (High Dynamic Range) display technology allows HDMI 2.0a great improvements in light/dark contrast, enhancing the picture quality for even more realistic representation. This function will be a standard in the new and modern 4K Ultra-HD models, making everything even more vivid.
- A highlight for all gamers out there: HDMI 2.0 Dual View – makes for an incredible gaming experience!
Dual View is the new standard in all 3D TVs. Instead of displaying with split-screen view, the new function allows two completely different HD videos streams to be shown on the same screen at the same time. For gamers this means no more split screen when wearing 3D glasses. Each player will only see their screen, in full TV screen size, although watching the same TV.
This feature does not yet exist for movies though. But don’t worry! We’re sure that this will be implemented pretty soon.
- Multi-Stream-Feature with HDMI 2.0
With HDMI 2.0 you can listen to 4 different audio streams at the same time – a great feature for the internationally connected and language buffs. For instance, someone can watch a movie in German, and at the same time, someone else can watch it in English on the same screen.
HDMI 2.0 is backward compatible, which means that you won’t have to buy new cables in order to connect your new standard. The cables that worked with your old HDMI versions, will also work with the new, as long as the device itself has HDMI 2.0.
So, Don’t Throw Away Your HDMI Cables
Because generally, all HDMI cables are compatible with all HDMI versions and thus interchangeable. Only when it comes to 4K resolution or 3D, a bigger capacity is needed.
To help you understand, have a look at this short overview:
- Standard HDMI Cable: designed to handle HD videos and audio, up to 1080i and 720p
- Standard HDMI Cable with Ethernet: see above, but also includes HDMI Ethernet Channel (for device networking)
- High Speed HDMI Cable: designed to handle 3D and 4K, 1080p and deep color
- High Speed HDMI Cable with Ethernet: see above, but also includes HDMI Ethernet Channel (for device networking)
- Standard Automotive HDMI Cable: perfect for automotive use, smaller connectors
Also: always note the connector types for HDMI.
4 Connector Types for Your HDMI Connections
Type A, B, C and D:
Type A and Type B count as regular connectors for all initial HDMI versions, with HDMI Type A for TVs and Blu-ray player being the standard. Type C, a smaller connector, is also called mini-HDMI connector. This type is perfect for mobile usage and smaller devices. The even smaller connector Type D, or micro-HDMI connector, is generally used for smartphones and tablets.
Type C mini-HDMI cables and type D micro-HDMI cables can be converted to regular HDMI cables with the help of adapters and also used as such. There are also special connectors for the use in the car, to better secure the HDMI cable in a moving vehicle (Automotive Connection System).
The HDMI Future is Bright
So, what kind of high quality entertainment can we expect in the future? There are definitely exciting and innovative technologies on the horizon! It is already possible to stream realistic, clear and crisp video and audio data with a wireless HDMI connection, giving us a flexible and modern home theater and no more tangled wires. Unfortunately, most available devices are not yet ready for this technology. So for the moment, we can still rely on our current HDMI cables to connect.
The industry is already providing adapters that can be plugged into the HDMI output at the sender and into the HDMI input at the TV or player, but regular consumers still have to wait until our HD, 4K and 3D ready devices can bring wireless HDMI connection into the home theater. It’s a huge question of price.
Also discussions around 8K, which would give us eight times the resolution of Full HD, hints to exciting future innovations. Even though the Chief Product Officer Neil Hunt of the streaming giant Netflix indicated in a statement, that the future of TV is not in increasing the number of pixels, but in simply increasing the quality of them. So, we’re definitely excited for the future!
Until then, you will be able to find all necessary information about bandwidth, the different video-, audio- and color formats and all other designations and specifications that you need for your very own HDMI experience, here.
Overview of HDMI Specifications
Our advice: always keep an eye on the listed informations and specifications
on the back of the device when purchasing.
Because not every Ultra-HD TV has to necessarily include all specifications of
a specific HDMI version.
We’re more than happy to help if there are any further questions. So don’t hesitate to reach out to us for assistance in finding the right playback device for your projects.